
Bridging the Gap: How Tech Domain Experts Can Thrive as AI Practitioners
Zaheer Aziz
The Role of an AI Practitioner
Why Domain Experts Need AI
Traditional methods, although effective, are often time-consuming and prone to inefficiencies. The integration of AI tools can transform these processes, offering faster, more accurate, and scalable solutions. Here’s how AI can revolutionize various aspects of technical work:
• Networking: AI can automate network management tasks, optimize traffic flow, generate new requirements and designs, and predict potential failures before they happen, ensuring smoother and more reliable operations.
• Cybersecurity: With AI tools, cybersecurity professionals can quickly detect and respond to threats, analyze vast amounts of data for potential vulnerabilities, and automate routine security checks, enhancing overall security posture.
• Collaboration: AI tools can facilitate better collaboration notes and action items taking, real-time translation, and enhanced communication analytics, making teamwork more efficient and productive.
• Project Management: AI can assist in project management delivery life cycle by providing predictive analytics, avoid scope creep, automating administrative tasks, and offering insights based on data trends, enabling better decision-making and profitable project delivery.
Overcoming the Overwhelm
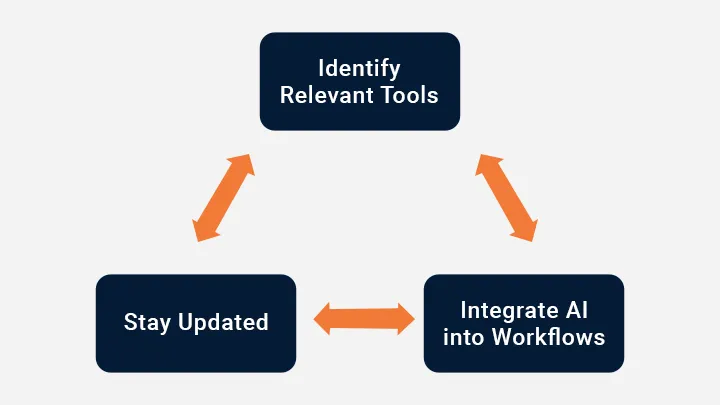
1. Identify Relevant Tools: Evaluate and select AI tools that align with their specific needs and challenges. This requires an understanding of both the domain and the capabilities of available AI solutions.
2. Integrate AI into Workflows: Seamlessly incorporate AI tools into existing processes to enhance efficiency and accuracy. This could involve using generative AI for drafting documents, leveraging AI-driven automation for repetitive tasks, or employing AI analytics for better insights.
3. Stay Updated: The AI landscape is continuously evolving, with new tools and capabilities emerging regularly. “AI Practitioner” need to stay informed about the latest developments and be adaptable to integrate new solutions as they become available.
Practical Applications and Examples
• Documentation: Generative AI can assist in drafting documents, reducing the time and effort required for manual writing and ensuring consistency and accuracy.
• Automation: AI can be used to automate software development tasks, such as code generation and testing, freeing up time for developers to focus on more complex problem-solving.
• Product Development: Companies can embed AI capabilities into their products, offering enhanced features and functionalities to end-users. “AI Practitioner” play a key role in identifying and integrating these AI enhancements.
• Observability: AI-powered observability platforms can simplify monitoring and management by providing intuitive interfaces and automated insights. For example, instead of manually checking logs and running commands, AI can automate these tasks and present the results in an easily understandable format.
Conclusion


